UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are two terms that have been tossed around in the digital world and are often misdefined or not defined, to begin with. The implication though is that these two terms carry different, although complementing facets of design which are significant in the formulation of functional and interesting digital products. In order to learn more about the distinction between the two and how they can benefit each other, we will explore the specifics of UI and UX design.
What is UI Design?
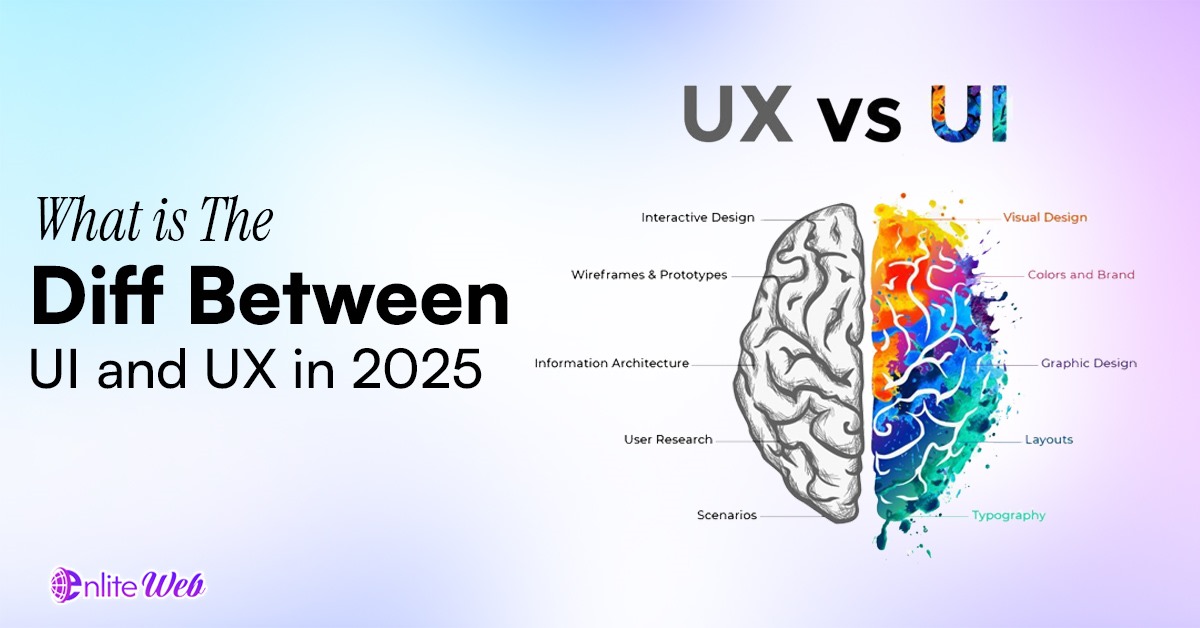
The design of the User interface (UI) is what the human talks about when it comes to visual and interactivity of a product used. It is all that users see on a digital platform including buttons and icons, navigation menu and sliders. The UI design is concerned with the appearance and the feel of the interface, making it visually attractive, easy to use, and similar in appearance across platforms and devices.
After finding the best possible version-the wireframes (which is a simple blueprint of how the page should look), UI designers turn them into something beautiful that still manages to work very effectively. The aim of UI design is to make a visually congruent experience to the user, so that each element of the interface is functional with all the other elements of the interface.
Key Aspects of UI Design
- Visual Design
UI design aims at the visual appeal of a product. These aspects incorporate the utilization of colours and layout as well as typography to compose a design which is both interesting to the eye and intuitive in navigation. Good visual design promotes the usage of the product by the user since the product is intuitive and pleasant. - Interactivity
Interactivity of the interface, i.e. the presence of buttons, sliders, and toggle switches, is also addressed in UI design. All these aspects must be seen clearly and are not difficult to use since the users are able to play with the product. - Responsiveness
Since users are accessing digital products through various products, UI design should consider designing the interface in a way that allows it to fit in sizes and transverse across screen sizes. The interface must be responsive and offer the same experience to the user regardless of whether one uses a mobile phone, a tablet, or the desktop. - Prototyping
The process in which UI designers make prototypes will give an idea of how the interface will actually look once it is finished. When a designer uses prototypes, he or she can be able to test interaction, steps, animations, and layouts prior to creation of the final product. That is beneficial in the detection of any possible problems in the initial stages and the optimization of the user interface to become easier to use.
What is UX Design?
The User Experience (UX) design is concerned with the experience that a user might have when using a product or service. It involves all the points where a user interacts with a product, including the moment when the user gets to hear about a product and the moment when he or she accomplishes the objectives. UX design is simply about creating a product or deliverable, which is user-friendly and which offers a value to the consumer.
Whereas UI design is more on the visual design of the interface, UX design tends more on the functionality of the whole product and its usability. It is the process of learning about the needs, behavior and pain areas of its users to come up with a product that effectively addresses their problems and in the most efficient manner possible.
Key Aspects of UX Design
- User Research
The knowledge of the users is one of the cornerstones of the UX design. UX designers do research to know the needs, behaviors and preferences of target audience. This study assists in designing a product that meets the expectations of the users and satisfying their needs. - Wireframing
Wireframing refers to the creation of a rough basis of the product. UX designers draw the flow and design of the interface in terms of how they are going to make the user interface. UI designers have the tendency to use wireframes as a reference point where they can create their design. - Usability Testing
If the product is designed of course, the next thing that UX designers can do is to test it in the hats of the real users to collect feedback. What usability testing achieves is to point to the points at which users are experiencing difficulties and gives some clues on how to enhance the overall experience of using the product as well as enhance its functionality. - User Journey Mapping
UX designers draw the user journey to gauge their behaviour at each point of interaction with the product. This process aids in making sure that users find access to the product easy and that their goals can be attained with ease without subjecting them to unnecessary challenges.
Key Differences Between UI and UX Design
Although UI and UX are constantly mentioned in regard to each other, two functions signify two different roles in the product development process. Their major differences can be separated in the following way:
1. Focus
- UI Design: Concentrates on the visuals of form and design of the product. It will make the product pleasing to appearance, uniform, and simple to browse through.
- UX Design: Concentrated on user experience of the whole product. It makes sure that the product can be utilized, friendly, and satisfies the consumer base.
2. Purpose
- UI Design: The primary goal of UI design is to create an interface that is visually appealing and easy to interact with. UI design aims to make the user’s interaction with the product as smooth and intuitive as possible.
- UX Design: The goal of UX design is to enhance the user’s overall experience with the product by ensuring it is easy to use, efficient, and meets their needs.
3. Approach
- UI Design: The visual UI designers concern themselves with buttons, icons, and typography. They concentrate on the appearance of the product and on the ease of usage of the interface.
- UX Design: UX designers are more holistic as they emphasize the journey of the user at large. They do researching, develop wireframe and develop user flows to make sure that the product is usable and can fulfill the expectations of the users.
4. Tangibility
- UI Design: UI design is more concrete, it is related to specific things which a user can view and is able to interact with.
- UX Design: UX design is not a very tangible concept and is more concerned with the intangible part of user experience like what it is easy to achieve or things the user felt satisfied with.
How UI and UX Work Together
Whereas UI and UX differ, they have to be in constant cooperation with each other in order to produce a successful product. A user interface can only be successful as the user that it supports. No matter how beautiful it is designed, a difficult-to-use product is doomed and a beautiful one should not be used; on the contrary, it should be abandoned.
Suppose, there is a shopping app that has a well-designed interface yet tricky navigation. Regardless of how pretty the app would appear, people will not be able to buy something easily. On the same note a user-friendly app which has a complicated and ugly design will not attract the user interface and impressions.
In the product developed thoughtfully, the UI and UX work together and guarantee the viewer an attractive and effective interface and a comfortable and predictable experience, as well.
Is There Such a Thing as a UI/UX Designer?
As the functions of the UI and UX designers overlap, it is not rare to see many companies mix the two roles into a single job post. A UI/UX designer encompasses more than just how the product looks (visual design) to include all aspects of how a user will tangibly experience using the product (user experience). But, relatively bigger organizations tend towards having these two functions divided, particularly when the project is larger and more complicated.
Although one may be a UI/UX designer, what should be considered is that the two are different in terms of the skills they need. The UI designer is more likely to be good at graphic design, visual communication, whereas a UX designer has the skills to research and solve problems.
Which Career Path Should You Take: UI or UX Design?
When you choose between the UI and UX design, it is essential to look at your preferences and capabilities:
- On the other hand, UI design might be more suitable to you in case you enjoy working with images, making things attractive, and are a fan of graphic design.
- UX design could be the answer to you, in case you like to comprehend human behavior, carry out studies, and integrate awareness issues.
Another possibility is to become specialized in both fields, and nowadays, most designers are both UI and UX designers. It is better to have some minimum knowledge of both jobs, in case of small teams or start-ups, when one designer can be required to do both.
Conclusion
UI and UX design are two closely associated specialties without which the digital products are unlikely to succeed. Whereas UI is targeted at the visual and interactive interaction, UX is interested in the general user experience. These two areas have their distinct abilities and hence they need to be hand in hand so that the item produced is appealing to the eye and convenient to use.
Getting to appreciate the differences and relationship between UI and UX design may allow you to make a choice on the career to take or how to incorporate the two fields within your team. No matter whether you are a UI designer or a UX designer (or even both), these principles should help you to make successful products that leave the customers delighted.
This gives you an advantage of making both the aesthetics and the functionality of a product in such a way that your design will encourage users and will give them a pleasant and easy experience and they will like to have it in future.